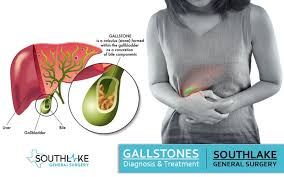
Gallstones are small, hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located just beneath the liver. The gallbladder is responsible for storing bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver that helps break down fats in the small intestine. While many people with gallstones experience no symptoms, the presence of these stones can cause a range of problems, including severe pain and complications that may require medical treatment.
In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gallstones, as well as some tips for preventing this condition.
Causes of Gallstones
Gallstones develop when there is an imbalance in the substances that make up bile. The three main components of bile are cholesterol, bilirubin, and bile salts. When one of these substances is present in excess, it can harden into a stone-like deposit. The exact cause of this imbalance is not known, but there are several factors that can increase the risk of developing gallstones, including:
- Age: Gallstones are more common in people over the age of 40.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop gallstones than men.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can increase the risk of gallstones.
- Family history: If other members of your family have had gallstones, you may be at increased risk.
- Rapid weight loss: Losing weight too quickly can increase the risk of gallstones.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at higher risk of developing gallstones.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as those used to lower cholesterol, can increase the risk of gallstones.
Symptoms of Gallstones
Many people with gallstones experience no symptoms. However, if a gallstone becomes lodged in a duct leading from the gallbladder, it can cause severe pain and other symptoms, such as:
- Pain in the upper right side of the abdomen that may radiate to the back or right shoulder blade
- Nausea and vomiting
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes)
- Fever and chills
- Clay-colored stools
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately, as gallstones can cause serious complications if left untreated.
Treatment Options for Gallstones
If you have gallstones but are not experiencing any symptoms, your doctor may recommend a wait-and-see approach, as many gallstones do not require treatment. However, if you are experiencing symptoms or complications, there are several treatment options available.